Techniques for NTFS File Recovery
File recovery refers to scanning a specific drive or folder and retrieving deleted files or entries located in the Master File Table (MFT).
It can also be described as the process of recovering or retrieving data which has been accidentally or deliberately damaged or corrupted from an inoperable or malfunctioned hard drive.
In this guide, we’ll talk about different NTFS file recovery techniques and how to troubleshoot your PC, if it’s unable to boot.
We’ll also walk you through how to recover your precious files in the event of accidental deletion or corruption of the hard drive’s partitions.
Drive recovery when MBR is damaged
The MBR, commonly referred to as the Master Boot Record, is the first sector on the hard drive that contains all the code enabling the computer to boot.
It is automatically created when the hard drive is partitioned during the installation of a Windows operating system. MBR is not located in a particular partition; therefore, storage media, like USB drives, cannot contain MBR.
It can be addressed as Cylinder: 0, Head: 0, Sector: 1.
An MBR error means that you cannot boot into your system. This occurs when the corrupted MBR is unable to locate the operating system on the hard drive.
Usually, when MBR is damaged, you will get a black screen during the boot process, alongside an error message that the operating system cannot be found.
Causes of MBR corruption
Several reasons can cause MBR corruption, including virus infection, MBR overwriting, drive failure, or deletion of a partition in a dual boot setup.
While MBR errors can be quite frustrating, they can easily be fixed using a disk repair DVD.
Symptoms of a corrupted MBR
If your hard disk has a corrupted MBR, your computer may not boot.
Instead, you will get a black screen shortly after loading the BIOS screen with an error message such as “Error Loading Operating System” or “Missing Operating System”.
Unfortunately, this error persists until you reboot and fix the problem.
How to remedy a corrupted MBR
To fix this error, you need to use the recovery tool found on your Windows 10 / 7 installation CD / DVD.
To begin with, insert the installation DVD and reboot your system. Remember to edit the boot priority order so that the system boots into the installation media.
On the first screen that appears, click the ‘Next’ button. If taken to the second screen, click on the ‘Repair’ option:

In the subsequent screen, select the ‘Troubleshoot’ option:
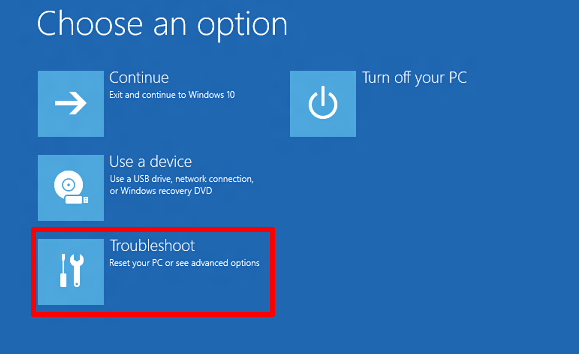
In the next screen, click on the ‘command prompt’ option, and run the following command:
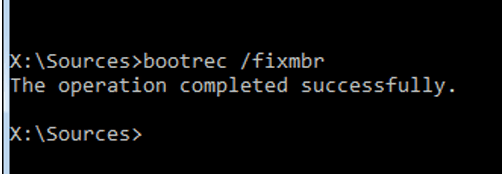
bootrec /fixmbr
The command fixes problems arising from a corrupt or damaged MBR. If all went well, you will get a confirmation message that the operation was successful:
Next, run the command below to erase the boot sector and create a new one:
bootrec /fixboot
If you have multiple operating systems on your hard drive, use the following ‘scanos’ argument to scan all missing operating systems to the boot config data:
bootrec /scanos
Lastly, you can now restart your system and see how it boots using Windows!
NTFS File Recovery
What causes file corruption or damage?
Here are some reasons that can cause data corruption in the hard drive:
- Hard drive’s mechanical failure
- Virus infection
- Damaged sectors on the hard drive
- Abrupt power outages when processing files
Symptoms of file corruption or data loss
There are several symptoms of file damage or corruption. Mostly, such errors are usually preceded by the blue screen of death (BSOD) prompts, abrupt system shut downs, and frequent crashing of programs.
This hinders the hard drive from processing requests, leading to file damage.
Often, corrupted files’ parent programs will decline to open them.
You are likely to get different error messages such as “file format not recognized,” or “this file name is not recognized”.
Files and directories can also disappear completely, and your operating system may point to damaged sectors when declining to run specific commands.
If you are using a physical hard drive, unlike the SSD, you may experience some noisy clicking sounds, excessive rattling or vibration of the hard drive, among other symptoms.
If you observe any of these issues, then you need to shut down your PC immediately.
NOTE:
- DO NOT attempt to write data on the damaged drive, as this will greatly reduce chances of recovering data successfully.
After powering off your PC, take out the entire hard drive and plug it into another computer on which data recovery software has been installed. Alternatively, you can use a data recovery software that doesn’t need any installation. A perfect example is file recovery software that can be run from a USB/pen drive.
- DO NOT save recovered data on the same drive you are trying to recover from.
When retrieving data from corrupted or damaged hard drives, you should refrain from saving it back to the affected disks, as there’s a high likelihood of overwriting the FAT and MFT records.
To be on the safe side, it is highly recommended to save the recovered data on another removable hard drive, USB drive, or network location.
Data Recovery applications
A data recovery application scours the hard drive, locates deleted and corrupted data, and pieces it back together.
The best and professional recovery tools will provide an overview of the recovered data, which may include images, video files, music files, documents, and spreadsheets.
Data recovery software can also restore zipped or compressed files and emails. You can recover files from hard drives, USB drives, camera, memory cards, and many more.
Here are some examples of professional data recovery software:
- Disk drill
- Recuva
- Ease US data recovery
- Undeletemyfiles Pro
Conclusion
No data recovery is 100% perfect; you may not recover all the lost files in your hard drive, especially where some files have been overwritten.
To avoid such situations of unprecedented loss or corruption of data, it’s always advisable to backup your data on the cloud or another remote location.
Do you want to prevent unauthorized deletion of directory objects or something similar to this problem?
Protect yourself and your clients against security leaks and get your free trial of the easiest and fastest NTFS Permission Reporter now!




Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!